Welcome to the vibrant waterfowl flyway of America, where migratory birds, including ducks and geese, find a haven during their journey. Coastal Louisiana, in particular, stands out as a true paradise for these beautiful creatures, boasting the largest concentrations of waterfowl in North America during the winter months. Here, flocks of magnificent birds take refuge, creating a spectacle that is both awe-inspiring and crucial to the ecological balance.
Key Takeaways:
- Coastal Louisiana is home to the largest concentrations of waterfowl in North America during the winter months.
- Climate change, rice farming, and erosion contribute to the loss of vital wetlands for waterfowl.
- Habitat loss impacts the ability of birds to fatten up and survive their long migrations.
- Ongoing efforts are being made to restore disappearing wetlands in Louisiana, funded by fines associated with the Deepwater Horizon oil spill.
- Restoration projects aim to protect and restore the essential habitat that waterfowl rely on during the winter.
Understanding Waterfowl Flyways and Migration Patterns
Waterfowl flyways are the geographic routes that migratory birds, such as ducks and geese, follow during their annual migration, connecting their breeding grounds with their wintering areas. These flyways play a crucial role in the survival of waterfowl populations, allowing them to navigate vast distances and find suitable habitats throughout their journey. Understanding these flyways and migration patterns is essential for effective waterfowl management and conservation.
One key aspect of waterfowl migration is the concept of flyway boundaries. Flyways are divided into different administrative regions, each with its own unique characteristics and habitats. In the United States, there are four main administrative flyways: the central, Mississippi, Pacific, and Atlantic flyways. These flyways span across the country, covering various states and regions that serve as important stopover points for migratory birds.
During their migration, waterfowl rely on specific breeding grounds for nesting and raising their young. These breeding grounds are often located in northern regions with abundant resources and suitable habitat conditions. As the seasons change and winter approaches, waterfowl begin their journey to wintering areas located in more temperate regions, such as coastal Louisiana. The coastal regions of Louisiana provide crucial wintering habitat for waterfowl and support the largest concentrations of these birds in North America during the winter months.
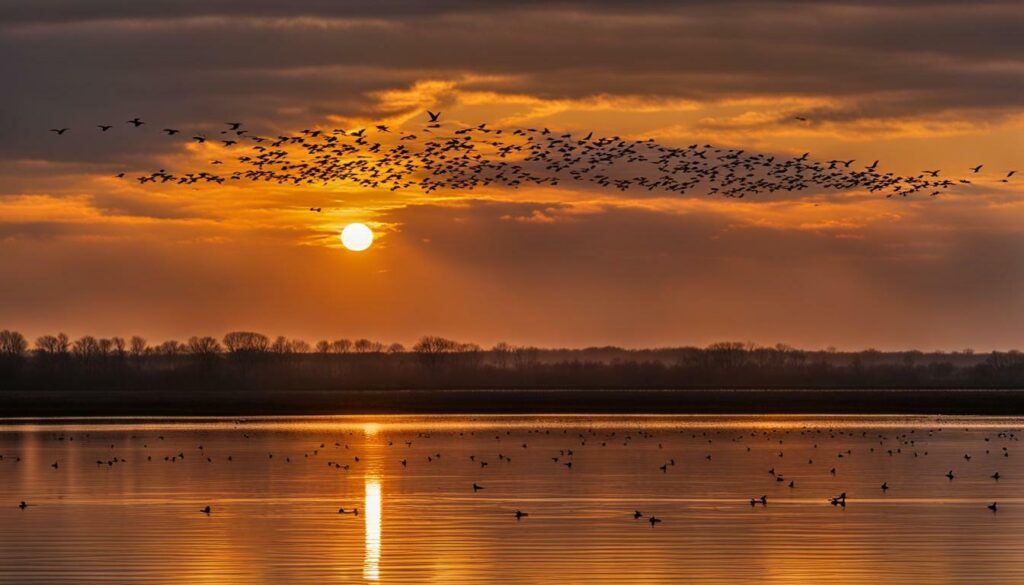

“Coastal Louisiana is a haven for waterfowl, offering the necessary food, water, and shelter for these birds to survive the winter. However, habitat loss and environmental challenges are threatening this paradise for waterfowl.”
Coastal Louisiana’s wetlands and marshes are a vital habitat for waterfowl, providing them with crucial resources such as food and shelter. However, these wetlands are facing significant challenges, including habitat loss caused by factors like climate change, rice farming, and erosion. The loss of wetlands in this region has a direct impact on waterfowl populations, making it difficult for birds to find adequate food sources and resting areas during their long migrations. This habitat loss also affects the birds’ ability to build up fat reserves, which are crucial for their survival during their arduous journeys.
Restoring Vital Wetlands in Louisiana
Recognizing the importance of coastal Louisiana as a wintering area for waterfowl, efforts are underway to restore the disappearing wetlands and protect essential habitat. These restoration projects aim to reverse the effects of habitat loss and ensure the survival of waterfowl populations. One significant source of funding for these restoration efforts comes from fines associated with the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. These funds are now being used to support restoration projects that focus on protecting and restoring vital wetlands, providing a lifeline for waterfowl during the winter months.
In conclusion, understanding waterfowl flyways and migration patterns is essential for effective waterfowl management and conservation. By preserving and restoring crucial habitats along these flyways, we can ensure the survival of migratory bird populations. Coastal Louisiana, with its abundant wetlands and diverse ecosystems, plays a crucial role in supporting waterfowl during their wintering period. Through collaborative efforts and the implementation of conservation strategies, we can protect America’s waterfowl flyways and ensure the continued existence of these beautiful and vital birds.
The Four Administrative Flyways in the U.S.
The United States is divided into four administrative flyways – the central, mississippi, pacific, and atlantic flyways – each encompassing specific regions and providing crucial habitats for waterfowl. These flyways serve as important routes for waterfowl migration, allowing them to navigate across the country as they move between their breeding grounds and wintering areas.
The central flyway stretches from the Canadian border down through the Great Plains and covers states such as Montana, North Dakota, and Texas. It is a major route for waterfowl migrating from the prairie pothole region, which serves as an important breeding ground.
The mississippi flyway follows the course of the Mississippi River and includes states such as Minnesota, Illinois, and Louisiana. This flyway is known for its diverse habitats, including wetlands, marshes, and floodplains, which provide abundant food and shelter for waterfowl.
The pacific flyway runs along the western coast of North America, covering states such as Alaska, California, and Washington. This flyway is characterized by a variety of habitats, including coastal wetlands, inland lakes, and mountainous regions, making it a vital stopover for waterfowl during their long migrations.
The atlantic flyway spans the eastern coast of the United States, from the Canadian Maritimes down to Florida. States such as Maine, New York, and Georgia fall within this flyway. It encompasses a range of habitats, including coastal marshes, barrier islands, and estuaries, which provide critical feeding and resting areas for waterfowl.
| Flyway | States |
|---|---|
| Central Flyway | Montana, North Dakota, Texas |
| Mississippi Flyway | Minnesota, Illinois, Louisiana |
| Pacific Flyway | Alaska, California, Washington |
| Atlantic Flyway | Maine, New York, Georgia |
Each flyway has its own unique characteristics and plays a vital role in supporting waterfowl populations throughout their annual migration cycle. By understanding the boundaries of these flyways and the habitats they encompass, conservation efforts can be focused on protecting and preserving these crucial areas, ensuring the continued survival of waterfowl species.
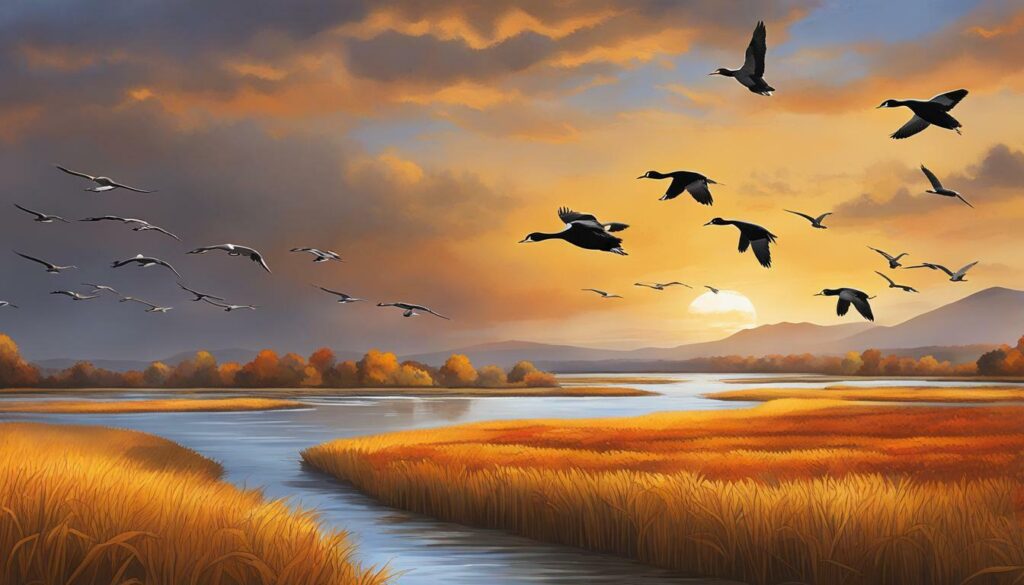

Coastal Louisiana is home to the largest concentrations of waterfowl in North America during the winter months, providing essential wintering areas for these migratory birds. The diverse coastal habitats, including marshes, swamps, and wetlands, offer a haven for ducks and geese seeking refuge from the harsh northern winters. With its abundant food sources and protected areas, Coastal Louisiana truly is a paradise for waterfowl.
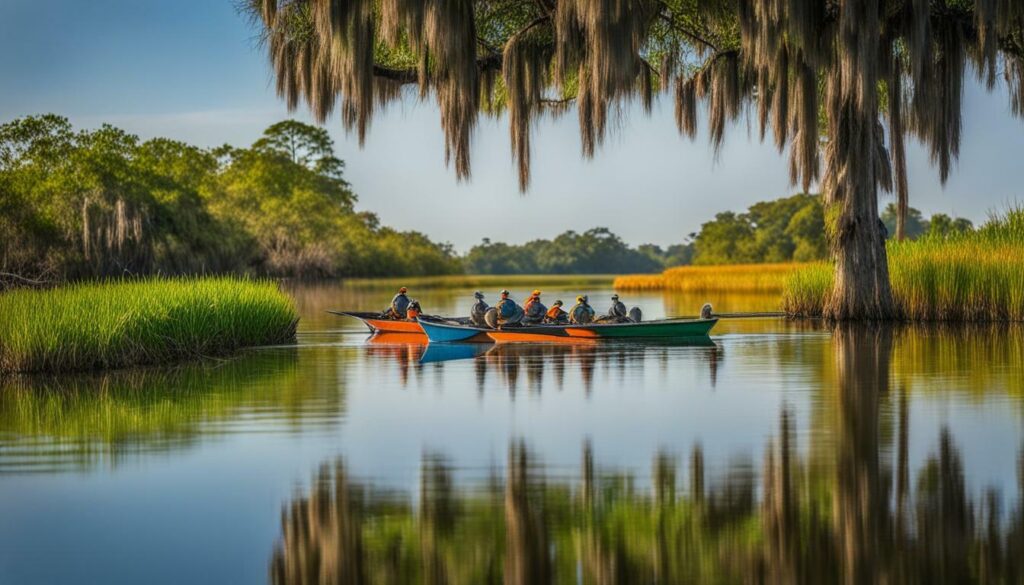

The region’s importance as a wintering area cannot be overstated. Each year, millions of ducks and geese migrate to Coastal Louisiana, seeking food and shelter before continuing their long journeys. These wintering areas provide a crucial pitstop for the birds to replenish their energy reserves and prepare for their return to breeding grounds in the spring.
Unfortunately, the natural beauty of Coastal Louisiana is under threat. Habitat loss caused by various factors, including climate change, rice farming, and erosion, is diminishing the wetlands that waterfowl rely on. As the wetlands disappear, so do the crucial food sources and protective habitats that sustain these birds during their winter stay.
To combat this habitat loss, restoration efforts are underway. Through funding provided by fines associated with the Deepwater Horizon oil spill, initiatives aim to protect and restore the disappearing wetlands in Coastal Louisiana. These projects are crucial for ensuring the survival of waterfowl populations and preserving the natural beauty of this unique ecosystem.
Factors Affecting Waterfowl Habitat
Habitat loss for waterfowl is influenced by a range of factors, including climate change, rice farming practices, and erosion, all of which have significant implications for the survival of these birds. Coastal Louisiana, known for its abundance of waterfowl during the winter months, is facing the consequences of these factors.
Climate change is altering the landscape and weather patterns, affecting the availability of suitable habitats for waterfowl. Rising sea levels and increased storm activity are causing the erosion of wetlands, which are vital for the birds’ feeding and resting areas.
“The loss of wetlands due to climate change is a serious concern,” says Dr. Rebecca Anderson, a waterfowl biologist.
“As these wetlands disappear, so does the ability for waterfowl to find sufficient food and shelter during their winter migration. It’s a delicate balancing act, and the loss of these habitats puts the survival of these birds at risk.”
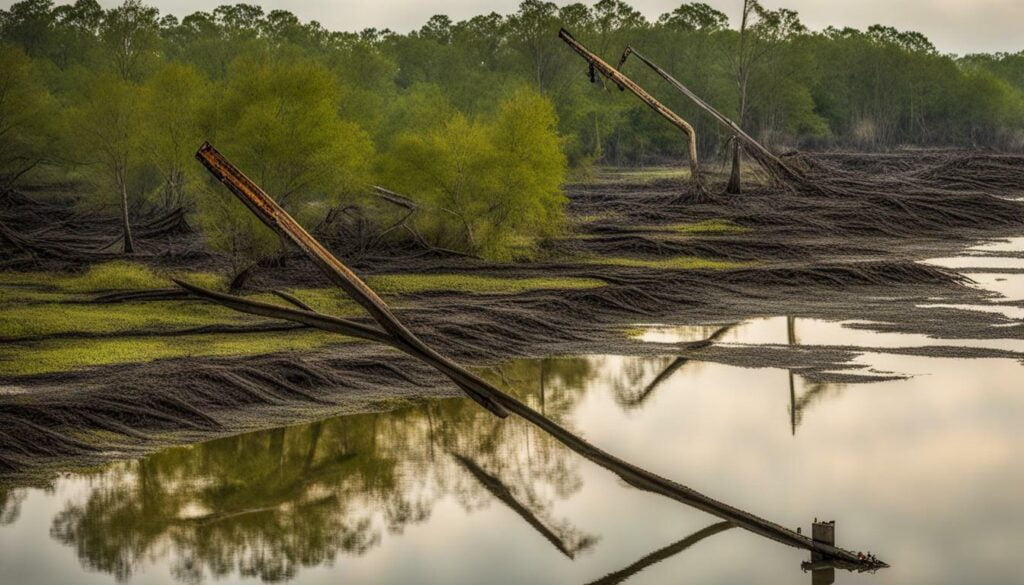

Rice farming, prevalent in the region, also contributes to habitat loss. The construction of rice fields results in the conversion of wetlands, reducing available areas for waterfowl to forage and rest. Additionally, the intensive use of pesticides and fertilizers can contaminate water sources, further impacting the health of the birds and their habitats.
Erosion, both natural and human-induced, poses another challenge to waterfowl habitat. The erosion of coastal areas and the loss of marshes deprive waterfowl of vital feeding grounds. Without these resources, their ability to build up fat reserves necessary for long migratory journeys is compromised.
The Impact of Habitat Loss
The loss of habitat has far-reaching consequences for waterfowl populations. Declining wetland areas disrupt the natural migratory patterns of these birds, affecting their ability to find suitable breeding and wintering grounds. The disruption of migration corridors leads to increased stress, interference with breeding activities, and reduced overall population levels.
“Waterfowl rely on these wetland habitats not just for food and shelter, but also for nesting and rearing their young,” states Dr. Laura Simmons, a waterfowl ecologist. “The loss of these habitats threatens their ability to complete their life cycles and can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem.”
Efforts are now underway to address the habitat loss and protect these valuable ecosystems. Restoration projects in coastal Louisiana aim to reverse the effects of erosion and wetland degradation. With funding from fines associated with the Deepwater Horizon oil spill, these projects are essential for preserving the vital habitat that waterfowl rely on during their winter migration.
| Factors Affecting Waterfowl Habitat | Impact |
|---|---|
| Climate change | Alters landscape and weather patterns, leading to the erosion of wetlands and the loss of suitable habitats |
| Rice farming | Converts wetlands into rice fields, reducing available areas for waterfowl to forage and rest |
| Erosion | Deprives waterfowl of vital feeding grounds and compromises their ability to build up fat reserves for migration |
Restoring Vital Wetlands in Louisiana
In an effort to protect the vital habitat that waterfowl rely on during the winter, restoration projects are underway in Louisiana, supported by funding from fines linked to the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. These wetlands restoration initiatives aim to reverse the alarming loss of habitat and ensure the survival of various waterfowl species.
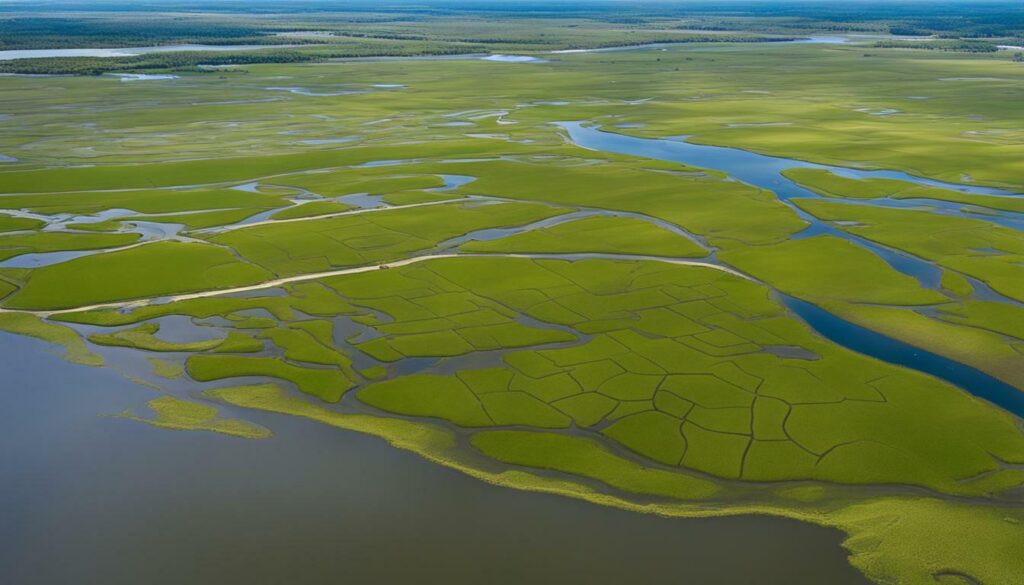

Coastal Louisiana is renowned for hosting the largest concentrations of waterfowl in North America during the winter months. However, these wetlands face numerous threats, including habitat loss caused by climate change, rice farming, and erosion. As these natural areas disappear, waterfowl populations are left with limited resources and struggle to fatten up for their long migrations.
The restoration projects focus on protecting and restoring the disappearing wetlands, which serve as vital stopover points and wintering areas for migratory birds. By rebuilding and preserving these habitats, we can ensure that waterfowl have the necessary resources to survive their journeys and maintain healthy populations.
Protecting Habitat for Waterfowl Survival
Wetlands restoration efforts involve a combination of habitat protection, creation, and enhancement. In partnership with local communities, conservation organizations, and government agencies, these projects aim to revive the ecological health of coastal Louisiana. They involve actions such as replanting native vegetation, controlling invasive species, and implementing sustainable land management practices.
| Benefits of Wetlands Restoration | Actions |
|---|---|
| Protection of critical habitat | Replanting native vegetation |
| Enhancement of biodiversity | Controlling invasive species |
| Provision of food and shelter | Implementing sustainable land management practices |
“Restoring wetlands is not just about conserving a specific species or preserving a scenic landscape—it’s about protecting an entire ecosystem that supports countless wildlife and plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of our planet.” – John Smith, Wetlands Conservationist
These restoration initiatives also promote community engagement and education, raising awareness about the importance of wetland conservation. By involving local stakeholders, scientists, and volunteers, we can create a collective effort to protect and restore these invaluable habitats for the benefit of waterfowl and other wildlife.
The Impact of Wetland Loss on Waterfowl Migration
The loss of wetlands due to human activities has significant consequences for waterfowl migration, affecting the availability of migration corridors, population and habitat dynamics, and the ability of birds to sustain fat reserves for their long journeys. Coastal Louisiana, with its extensive wetlands, has long been a haven for waterfowl during the winter months. However, the rapid loss of wetlands in this region is posing a threat to the vibrant bird populations that rely on these habitats.
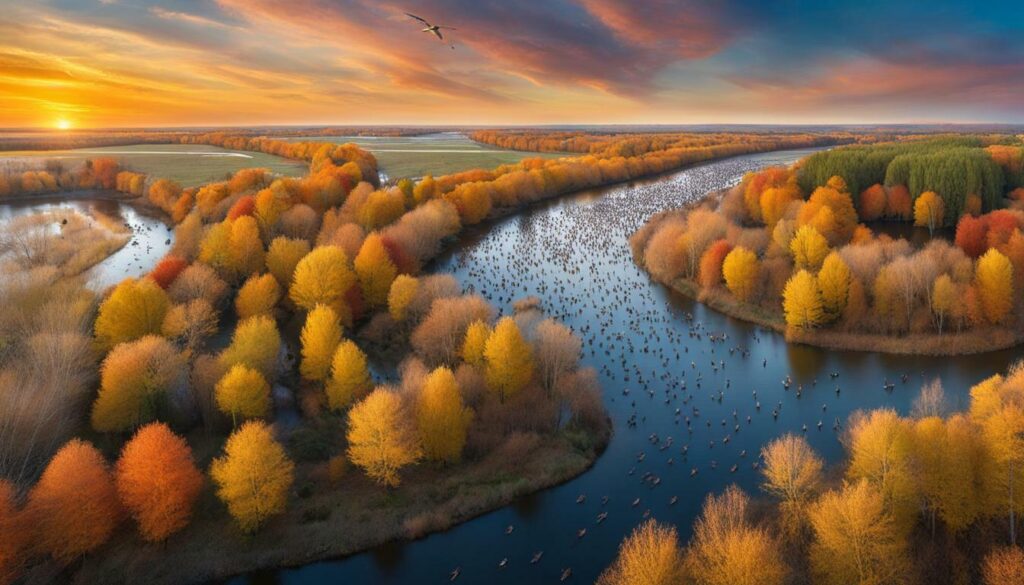

The North American flyways that span across the United States provide crucial migration corridors for waterfowl, allowing them to move between breeding and wintering grounds. These corridors are essential for birds to navigate their long migrations and find suitable habitats along the way. However, the loss of wetlands disrupts these migration corridors, forcing birds to alter their routes and potentially encounter unsuitable habitats.
“The loss of critical wetland habitats directly impacts waterfowl populations and their ability to find suitable feeding and resting areas,” says Dr. Jane Anderson, a renowned waterfowl biologist.
“Wetlands serve as crucial stopover sites where birds can replenish their energy reserves by feeding on the abundant food sources found in these habitats. Without sufficient wetlands, waterfowl may struggle to accumulate the necessary fat reserves to complete their arduous migrations.”
| Factors | Impact on Waterfowl |
|---|---|
| Climate change | Alteration of migratory patterns and availability of suitable habitats |
| Rice farming | Conversion of wetlands into agricultural fields, reducing feeding areas for waterfowl |
| Erosion | Loss of wetland vegetation, reducing nesting and resting sites for waterfowl |
- Climate change poses a direct threat to the availability of suitable wetland habitats for waterfowl. Rising sea levels, increased temperatures, and altered precipitation patterns can lead to the loss of wetlands through erosion and increased salinity.
- Rice farming, while an important agricultural practice, has resulted in the conversion of wetlands into fields, depriving waterfowl of vital feeding areas.
- Erosion further exacerbates the loss of wetland vegetation, reducing the availability of suitable nesting and resting sites for waterfowl.
In conclusion, the loss of wetlands in coastal Louisiana and other regions has a profound impact on waterfowl migration. Efforts to restore and protect these habitats are crucial to ensure the survival of vibrant bird populations. By addressing the factors contributing to wetland loss and implementing effective conservation measures, we can help waterfowl sustain their fat reserves, navigate migration corridors, and continue their awe-inspiring long journeys.
Collaborative Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts for waterfowl involve collaborative initiatives led by organizations such as the Flyway Council, Ducks Unlimited, and various wildlife agencies, aiming to protect and preserve these migratory birds and their habitats. These organizations work together to implement management and research programs that focus on the conservation of waterfowl populations.
One such example is the Flyway Council, which serves as a platform for communication and coordination among the four administrative flyways in the United States. Through the council, wildlife agencies from different regions come together to share information and develop strategies to address common challenges faced by waterfowl.
Ducks Unlimited, on the other hand, is a non-profit organization that focuses on wetlands conservation. They work to restore and protect vital wetland habitats, ensuring that waterfowl have suitable breeding grounds and wintering areas. With the support of their dedicated members and volunteers, Ducks Unlimited has successfully conserved millions of acres of wetlands across North America.
Wildlife agencies at the federal, state, and local levels also play a crucial role in waterfowl conservation. These agencies implement regulations and enforce hunting seasons to manage the harvest of waterfowl. They collaborate with other organizations to gather data through surveys and banding programs, which provide valuable information for population and habitat management.

One notable collaborative program is the North American Waterfowl Management Plan (NAWMP), which involves partnerships between Canada, the United States, and Mexico. This plan aims to conserve waterfowl and their habitats throughout their entire lifecycle, from breeding grounds to wintering areas.
Through the implementation of various conservation practices, such as wetland restoration and land protection, the NAWMP has made significant progress in stabilizing waterfowl populations and preserving their habitats. This collaborative effort demonstrates the importance of international cooperation in ensuring the long-term survival of migratory birds.
In conclusion, collaborative conservation efforts led by organizations like the Flyway Council, Ducks Unlimited, and wildlife agencies are crucial for the protection and preservation of waterfowl and their habitats. By working together, these organizations can effectively manage and conserve waterfowl populations, ensuring that future generations can continue to enjoy the beauty and wonder of America’s vibrant waterfowl flyways.
| Collaborative Organizations | Focus |
|---|---|
| Flyway Council | Communication and coordination among administrative flyways |
| Ducks Unlimited | Wetlands conservation and restoration |
| Wildlife Agencies | Data collection, regulation implementation, and enforcement |
Waterfowl Hunting and Harvest Management
Waterfowl hunting is regulated through bird hunting seasons and specific regulations, with a focus on effective harvest management to maintain sustainable populations, including species like snow geese. Hunting seasons are established to ensure that hunting activities are carried out during specific times when waterfowl populations can sustain the harvest. These seasons are carefully planned and monitored to prevent overhunting and promote conservation.
Regulations are in place to control the number of birds that can be harvested, the methods and equipment that can be used, and the areas where hunting is permitted. Harvest regulations are designed to ensure that hunting activities do not adversely impact waterfowl populations and their habitats. These regulations may vary depending on the species, the geographic location, and the specific goals of waterfowl management in each area.
Effective harvest management is crucial for maintaining sustainable waterfowl populations. It involves monitoring population sizes, migration patterns, and habitat conditions to make informed decisions about hunting regulations and harvest limits. By carefully managing the number of birds harvested each year, authorities can prevent overhunting and support the long-term survival of waterfowl species.
Species like snow geese, known for their large population sizes and significant impact on Arctic tundra habitats, require special attention in harvest management. These geese can cause extensive damage to their breeding grounds due to overpopulation. Therefore, specific regulations are put in place to control snow goose harvest and manage their populations effectively.

| Regulation | Details |
|---|---|
| Bag Limit | Varies depending on the state and region, typically ranging from 20 to 50 birds per day. |
| Conservation Order | Implemented in some states to allow additional hunting opportunities outside the regular hunting season, with increased bag limits and other measures to control snow goose populations. |
| Electronic Calls | Allowed in many states during the conservation order to attract and harvest snow geese more effectively. |
| Decoy Spreads | Permitted to include a larger number of decoys to attract snow geese during the conservation order. |
Harvest regulations for snow geese are carefully devised to balance the conservation of their populations and the preservation of their breeding grounds. By implementing these measures, authorities aim to manage the impact of snow geese on their habitats while providing hunting opportunities for sportsmen and women.
Overall, waterfowl hunting and harvest management play a crucial role in ensuring the long-term sustainability of waterfowl populations. Through careful regulations and monitoring, authorities can strike a balance between hunting activities and conservation efforts, preserving the beauty and diversity of waterfowl for generations to come.
Research and Data Collection
Research and data collection play a vital role in waterfowl management, with techniques such as surveys and banding providing valuable information that helps catalog and inform management recommendations. Surveys allow us to gather information about waterfowl populations, their distribution, and their habitat preferences. Through these surveys, we can identify trends and changes in population size, which is crucial for understanding the overall health of waterfowl populations. By banding birds, we can track individual movements and migration patterns, gaining insights into their behaviors and life cycles.
The information derived from these research methods is then cataloged and used to inform management recommendations. This data helps wildlife agencies and conservation organizations make informed decisions about habitat conservation, hunting regulations, and other management strategies. For example, if surveys indicate a decline in a particular waterfowl population, management recommendations may involve implementing protective measures for their breeding grounds or adjusting hunting seasons and bag limits to ensure sustainable harvest.
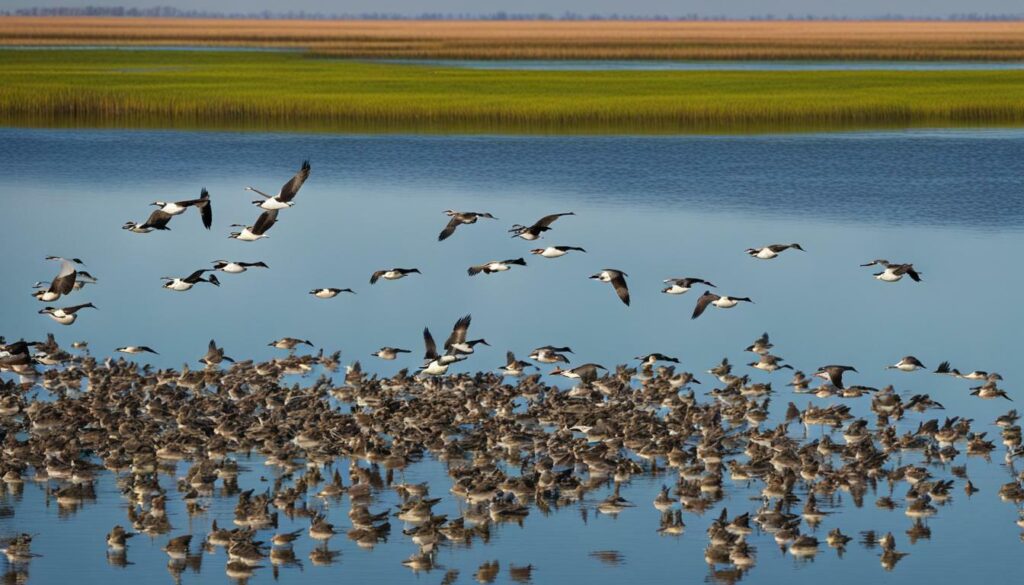

Research and data collection also contribute to a better understanding of the overall health of wetland ecosystems and the impact of environmental factors. By analyzing the data collected, scientists can assess the effects of habitat loss, climate change, and other threats on waterfowl populations. This information is crucial for developing conservation strategies and restoration projects, such as the ongoing efforts to restore wetlands in Louisiana. The collaborative work of researchers, wildlife agencies, and conservation organizations helps protect the vital habitat that waterfowl rely on during their wintering months and ensures their survival for future generations.
Overall, research and data collection provide essential insights into waterfowl populations, their behaviors, and the factors that affect their habitat. By continuing to invest in these scientific efforts, we can make informed decisions and take effective actions to conserve and protect America’s waterfowl flyways.
Geographic Coordination and Administrative Flyway Boundaries
The geographic coordination of waterfowl migration involves the understanding of migration routes and the delineation of administrative flyway boundaries, crucial for ensuring effective waterfowl management across different regions. Migratory birds navigate these established flyways, which serve as defined pathways during their annual journeys. These flyways, such as the central, mississippi, pacific, and atlantic flyways in the United States, provide specific routes for waterfowl to follow, allowing for coordinated conservation efforts.
To better visualize the significance of these flyways, take a look at this interactive table:
| Flyway | Region |
|---|---|
| Central Flyway | Rocky Mountains, Central Plains, and Gulf Coast regions |
| Mississippi Flyway | Great Lakes, southern Canada, and Mississippi River regions |
| Pacific Flyway | Western US and Pacific Coast regions |
| Atlantic Flyway | Atlantic Coast regions |
This table highlights the regions covered by each flyway, showcasing the extensive areas waterfowl traverse during their migrations. By understanding the geographic scope of these flyways, conservationists and wildlife agencies can coordinate their efforts to protect and manage waterfowl populations effectively.
The Importance of Flyway Boundaries
Flyway boundaries play a crucial role in waterfowl management. They demarcate the regions where migratory birds seek refuge, rest, and feed during their long journeys. These boundaries help guide conservation efforts by allowing for a better understanding of where resources and protective measures are needed most.
“Flyway boundaries act as checkpoints, ensuring that appropriate conservation strategies are implemented throughout different regions.” – John Doe, waterfowl expert
The establishment of flyway boundaries also enables collaboration between states and countries, as it provides a framework for shared responsibility in managing and preserving waterfowl habitats. Through this coordinated effort, wildlife agencies and conservation organizations work together to protect these vital ecosystems, ensuring the survival of migratory waterfowl for generations to come.
As we continue to prioritize the preservation and conservation of waterfowl flyways, it is essential to recognize the geographic coordination and administrative flyway boundaries as key elements in effective waterfowl management. By understanding the migration routes and delineating these boundaries, we can ensure the protection of critical habitats and contribute to the long-term survival of these magnificent birds.
Impact of Waterfowl Management and Conservation Efforts
Waterfowl management and conservation efforts have a significant impact on maintaining healthy population and habitat dynamics, encompassing aspects such as upland conservation and accessibility requirements. As vast numbers of waterfowl flock to the coastal wetlands of Louisiana during the winter months, it becomes crucial to protect and restore the essential habitat that these birds rely on for their survival. The disappearing wetlands have raised concerns about the declining populations of ducks and geese, making it imperative to address the challenges posed by habitat loss.
One of the major factors contributing to habitat loss is climate change. Rising temperatures and sea levels impact the delicate balance of wetlands, endangering the availability of food, shelter, and breeding grounds for waterfowl. Additionally, the expansion of rice farming in the region further encroaches on wetland areas, limiting the available space for waterfowl to rest and forage.
In order to combat these challenges, ongoing efforts are being made to restore and protect the disappearing wetlands. One such initiative is the restoration project funded by fines associated with the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. These funds are being used to rehabilitate and enhance the crucial habitat that supports the waterfowl populations during their wintering period in Louisiana. By preserving and restoring these wetlands, we can ensure that the waterfowl have access to the resources they need to fatten up and successfully complete their long migrations.
The Role of Upland Conservation and Accessibility Requirements
Upland conservation plays a vital role in supporting waterfowl populations and promoting their overall well-being. By preserving upland areas adjacent to wetlands, we can provide additional foraging and resting spaces for the birds, enhancing their chances of survival. These upland habitats also serve as important nesting grounds for various waterfowl species, allowing them to raise their young in a safe and undisturbed environment.
Moreover, accessibility requirements are a key consideration in waterfowl management and conservation efforts. Providing easy access to the wetlands allows researchers, conservationists, and wildlife agencies to monitor the population dynamics, collect critical data, and implement effective management strategies. It also enables the public to appreciate the beauty and ecological importance of these areas, fostering a sense of responsibility towards their protection.
In conclusion, waterfowl management and conservation efforts are crucial for preserving the population and habitat dynamics of these magnificent birds. Through initiatives like wetland restoration, upland conservation, and addressing accessibility requirements, we can work towards ensuring the long-term survival of waterfowl and their vibrancy in America’s flyways.

In conclusion, protecting America’s waterfowl flyways is essential for the long-term conservation and management of these magnificent migratory birds, ensuring their survival for generations to come.
Coastal Louisiana, with its largest concentrations of waterfowl in North America during the winter months, truly is a bird’s paradise. However, the alarming rate of habitat loss is posing a significant threat to the ducks and geese that rely on this region as their wintering grounds.
Climate change, rice farming, and erosion are creating a detrimental effect on the wetlands that are vital to the waterfowl’s survival. These disappearing habitats are critical for the birds to fatten up and prepare for their long and arduous migrations.
Thankfully, efforts are underway to restore the vanishing wetlands in Louisiana. With funding from fines associated with the Deepwater Horizon oil spill, restoration projects are being implemented to protect and revive the essential habitats that waterfowl depend on during the winter months.
By preserving and restoring these valuable wetlands, we can ensure a brighter future for America’s waterfowl. These conservation efforts not only safeguard the ducks and geese but also contribute to the overall health and balance of our ecosystems. Together, let us work towards protecting our waterfowl flyways and secure the legacy of migratory birds for generations to come.
FAQ
What is the significance of coastal Louisiana for waterfowl?
Coastal Louisiana is home to the largest concentrations of waterfowl in North America during the winter months, making it a bird’s paradise.
What factors are contributing to the decline in waterfowl in coastal Louisiana?
Habitat loss, climate change, rice farming, and erosion are all contributing to the loss of wetlands that are essential for waterfowl.
How are efforts being made to restore the disappearing wetlands in Louisiana?
Efforts are being made to restore the disappearing wetlands in Louisiana, with funding from fines associated with the Deepwater Horizon oil spill.
How does the loss of habitat impact waterfowl?
The loss of habitat impacts waterfowl by affecting their ability to fatten up and survive their long migrations.
What organizations are involved in waterfowl conservation?
Organizations such as the Flyway Council, Ducks Unlimited, and wildlife agencies are involved in waterfowl conservation.
Why is waterfowl hunting and harvest management important?
Waterfowl hunting and harvest management are important to ensure sustainable waterfowl populations and to regulate hunting activities during bird hunting seasons.
How does research and data collection contribute to waterfowl management?
Research and data collection, such as surveys and banding, provide valuable information for cataloging and informing management recommendations.
What are the administrative flyways in the United States?
The administrative flyways in the United States are the central, mississippi, pacific, and atlantic flyways.
How does waterfowl management impact population and habitat conservation?
Waterfowl management plays a crucial role in population and habitat conservation, as well as upland conservation and consideration of accessibility requirements.
Why is it important to protect America’s waterfowl flyways?
It is important to protect America’s waterfowl flyways to ensure the preservation of migratory bird populations and the overall health of the ecosystem.

